Simularity has successfully detected anomalies using SAR imagery.
But first, let’s review what SAR imagery is:
Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) is a type of radar that uses advanced signal processing techniques to create high-resolution images of the earth’s surface from airborne or spaceborne platforms. Some of the benefits of SAR technology include:
All-weather capability: SAR can penetrate clouds, fog, and other atmospheric conditions that would obstruct other imaging technologies, making it possible to acquire images even in adverse weather conditions.
Day and night imaging: SAR operates in the microwave frequency range and is not affected by daylight or darkness, allowing it to acquire images around the clock.
High resolution imaging: SAR can provide high-resolution images of the earth’s surface, with resolutions as fine as a few meters, allowing for detailed analysis of features such as buildings, roads, and other infrastructure.
Detection of changes: SAR can be used to detect changes in the earth’s surface over time, making it useful for monitoring urban growth, deforestation, and other environmental changes.
Active imaging: Unlike passive imaging technologies such as optical and infrared cameras, SAR is an active imaging system that emits its own microwave energy to produce images, making it possible to image through obscurants such as smoke, dust, and foliage.
Wide area coverage: SAR can cover large areas quickly and efficiently, making it ideal for mapping and monitoring large regions.
These benefits make SAR a valuable tool for a wide range of applications, including military and intelligence, agriculture, environmental monitoring, disaster response, and many others.
In terms of anomaly detection using SAR imagery, there have been several notable cases in history where SAR images have been used to detect important changes or events:
Environmental monitoring: SAR images have been used to monitor and detect changes in the earth’s environment, such as deforestation, coastal erosion, and desertification.
Disaster response: SAR images have been used to quickly assess the damage caused by natural disasters, such as earthquakes, hurricanes, and tsunamis. The high-resolution images can provide valuable information to emergency response teams, helping to prioritize relief efforts and assess the extent of the damage.
Military and intelligence: SAR images have been used by military and intelligence agencies to monitor and track changes in the earth’s surface, such as the construction of new infrastructure, military installations, and weapons systems.
Agriculture: SAR images have been used to monitor and assess the health of crops, providing valuable information to farmers for irrigation and fertilizer management.
Urban development: SAR images have been used to monitor the growth and expansion of cities, providing valuable information for urban planning and management.
These examples demonstrate the wide range of applications for SAR images and the important role that they play in detecting and responding to changes and events in our world.
Simularity uses AI to detect anomalies and our technology supports SAR imagery too. Here’s how we do it, in this short video demo case study:
Case Studies of SAR Anomaly Detection
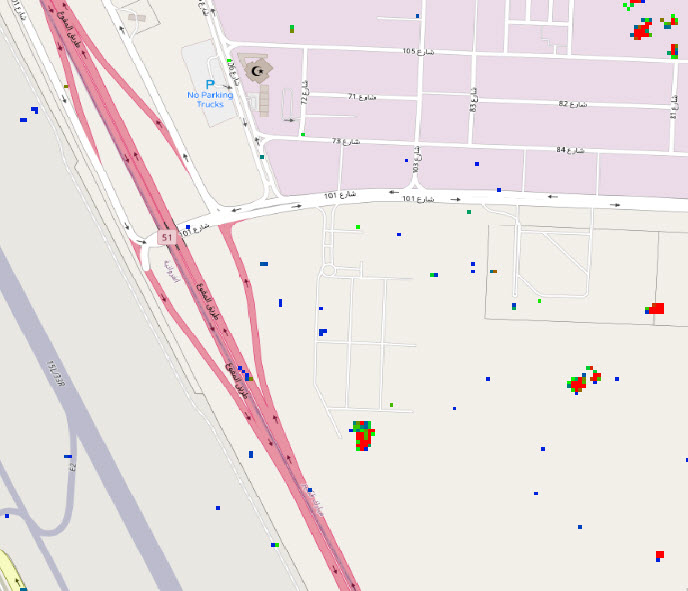
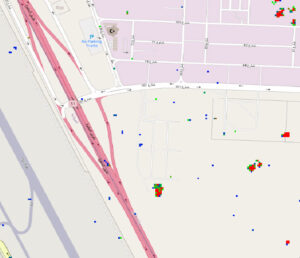
Simularity’s AIADS product has successfully analyzed SAR images to identify anomalies, such as this one. Here we see the “heatmap” for an oil refinery in Saudi Arabia, with the red areas showing the recent construction changes to the facility.

Our AI Driven Process
We have years of experience with AI and large image database technologies. Here is an overview of our process to manage the delivery of SAR anomaly images:
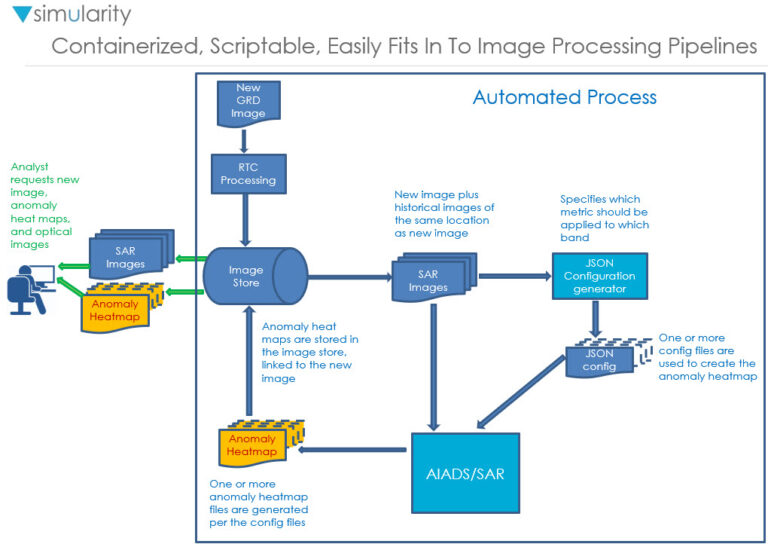
The main steps involved in processing SAR images for anomaly detection are:
- Collecting GRD Images from Supported Sensors
- We support all polarizations of SAR – HH HV VV VH. We can compute indices from them such as the VH/VV ration or the Radar Vegetation Index (RVI). For anomaly detection you typically want 2 or fewer bands (or indices) in the analysis – more bands reduce the resolution too much (although 3 can sometimes be useful).
- RTC Processing
- We process images to be Radiometrically Terrain Corrected (Analysis Ready). We can also process pairs of images using InSAR (Interferometric SAR) to generate a Digital Elevation Model (DEM). These pairs should be close together in time and not have large areas of differences.
- Configuration Generation
- Anomaly Image Generation
To explore how we can help you with your detection challenges, using SAR or Optical imagery, contact us today.